更多
党建思政
-
 2023-02-25校党委理论学习中心组集体学习习近平总书记重要讲话精神2月24日,校党委理论学习中心组开展集体学习,深入学习中共中央政治局会议听取近期疫情防控工作汇报有关情况和习近平总书记在中共中央政治局第三次集体学习时的重要讲话精神,研究部署我校学习贯彻工作。教育部党建工作联络员、中国石油大学(华东)原副校长孙海峰,全体校领导出席会议。会议由校党委书记王洪元主持。
2023-02-25校党委理论学习中心组集体学习习近平总书记重要讲话精神2月24日,校党委理论学习中心组开展集体学习,深入学习中共中央政治局会议听取近期疫情防控工作汇报有关情况和习近平总书记在中共中央政治局第三次集体学习时的重要讲话精神,研究部署我校学习贯彻工作。教育部党建工作联络员、中国石油大学(华东)原副校长孙海峰,全体校领导出席会议。会议由校党委书记王洪元主持。 -
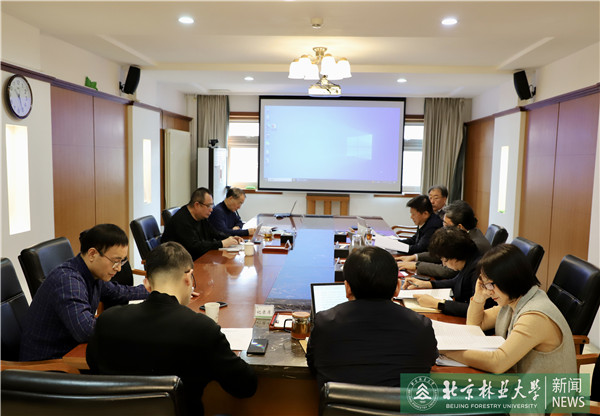 2023-02-16校党委理论学习中心组专题学习习近平总书记在学习贯彻党的二十大精神研讨班开班式上重要讲话精神2月16日,校党委理论学习中心组开展专题学习,深入学习领会习近平总书记在学习贯彻党的二十大精神研讨班开班式上重要讲话精神,研究部署我校学习贯彻工作。校党委书记王洪元主持会议。
2023-02-16校党委理论学习中心组专题学习习近平总书记在学习贯彻党的二十大精神研讨班开班式上重要讲话精神2月16日,校党委理论学习中心组开展专题学习,深入学习领会习近平总书记在学习贯彻党的二十大精神研讨班开班式上重要讲话精神,研究部署我校学习贯彻工作。校党委书记王洪元主持会议。 -
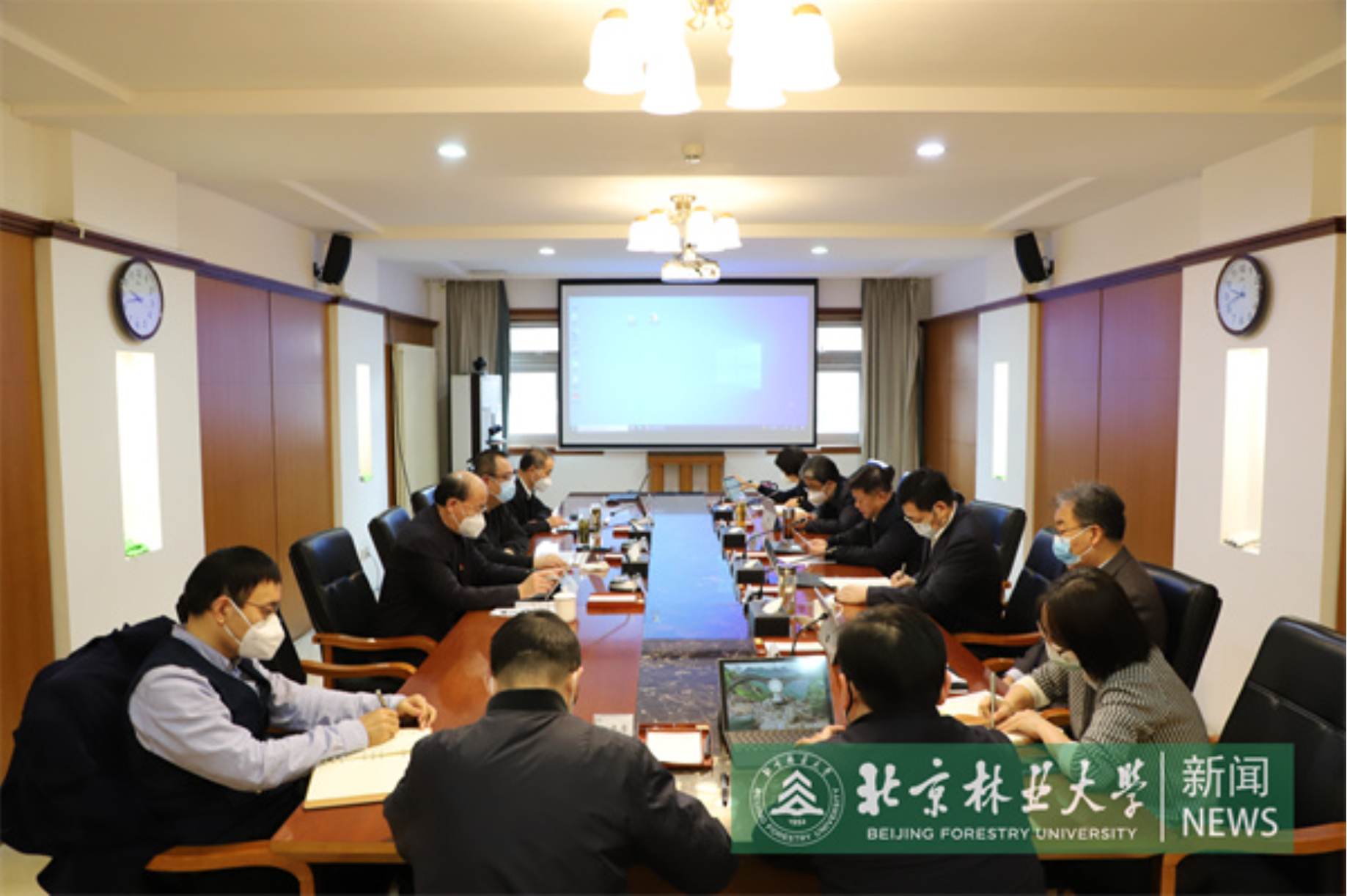 2023-01-08校党委理论学习中心组集体学习习近平总书记在中央政治局民主生活会上的重要讲话精神1月6日,校党委理论学习中心组开展集体学习,深入学习习近平总书记在中央政治局民主生活会上的重要讲话精神,研究部署我校学习贯彻工作。校党委书记王洪元主持会议。
2023-01-08校党委理论学习中心组集体学习习近平总书记在中央政治局民主生活会上的重要讲话精神1月6日,校党委理论学习中心组开展集体学习,深入学习习近平总书记在中央政治局民主生活会上的重要讲话精神,研究部署我校学习贯彻工作。校党委书记王洪元主持会议。 -
 2022-12-27校党委理论学习中心组集体学习中央经济工作会议精神和北京市委十三届二次全会精神12月26日,校党委理论学习中心组开展集体学习,深入学习中央经济工作会议精神和中国共产党北京市第十三届委员会第二次全体会议精神,研究部署我校学习贯彻工作。校党委书记王洪元主持会议。
2022-12-27校党委理论学习中心组集体学习中央经济工作会议精神和北京市委十三届二次全会精神12月26日,校党委理论学习中心组开展集体学习,深入学习中央经济工作会议精神和中国共产党北京市第十三届委员会第二次全体会议精神,研究部署我校学习贯彻工作。校党委书记王洪元主持会议。
-
252023-02
-
082023-01
-
272022-12
更多
教学科研
-
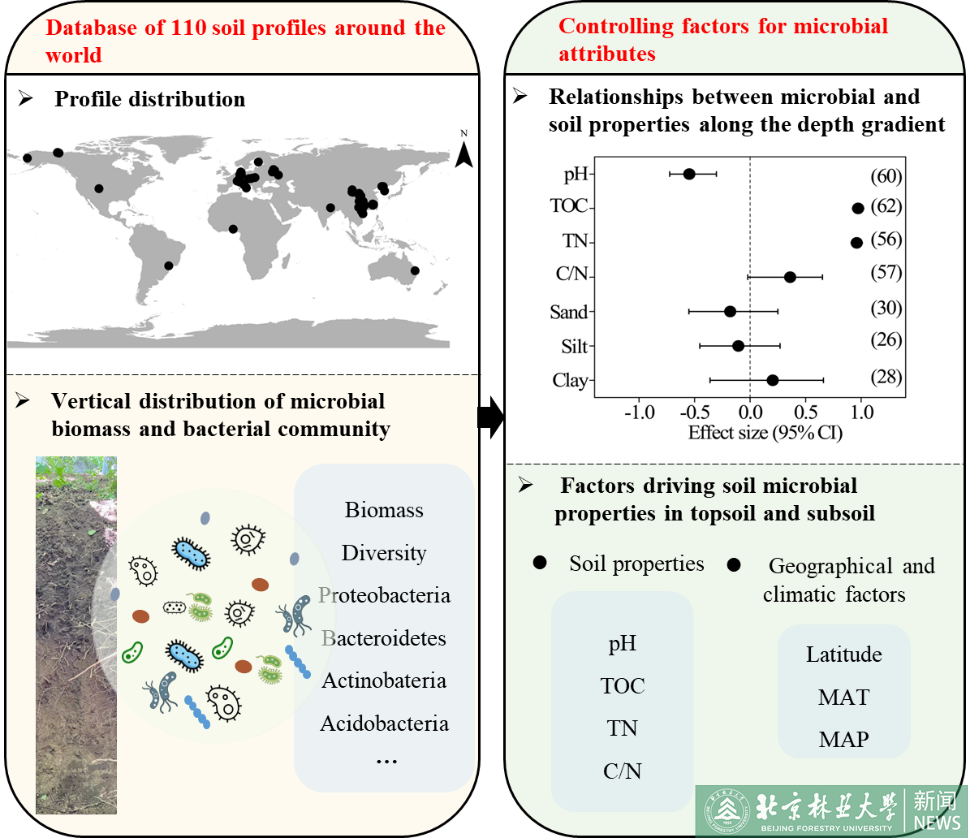 林学院团队在土壤微生物领域取得研究进展2023.0301
林学院团队在土壤微生物领域取得研究进展2023.0301 -
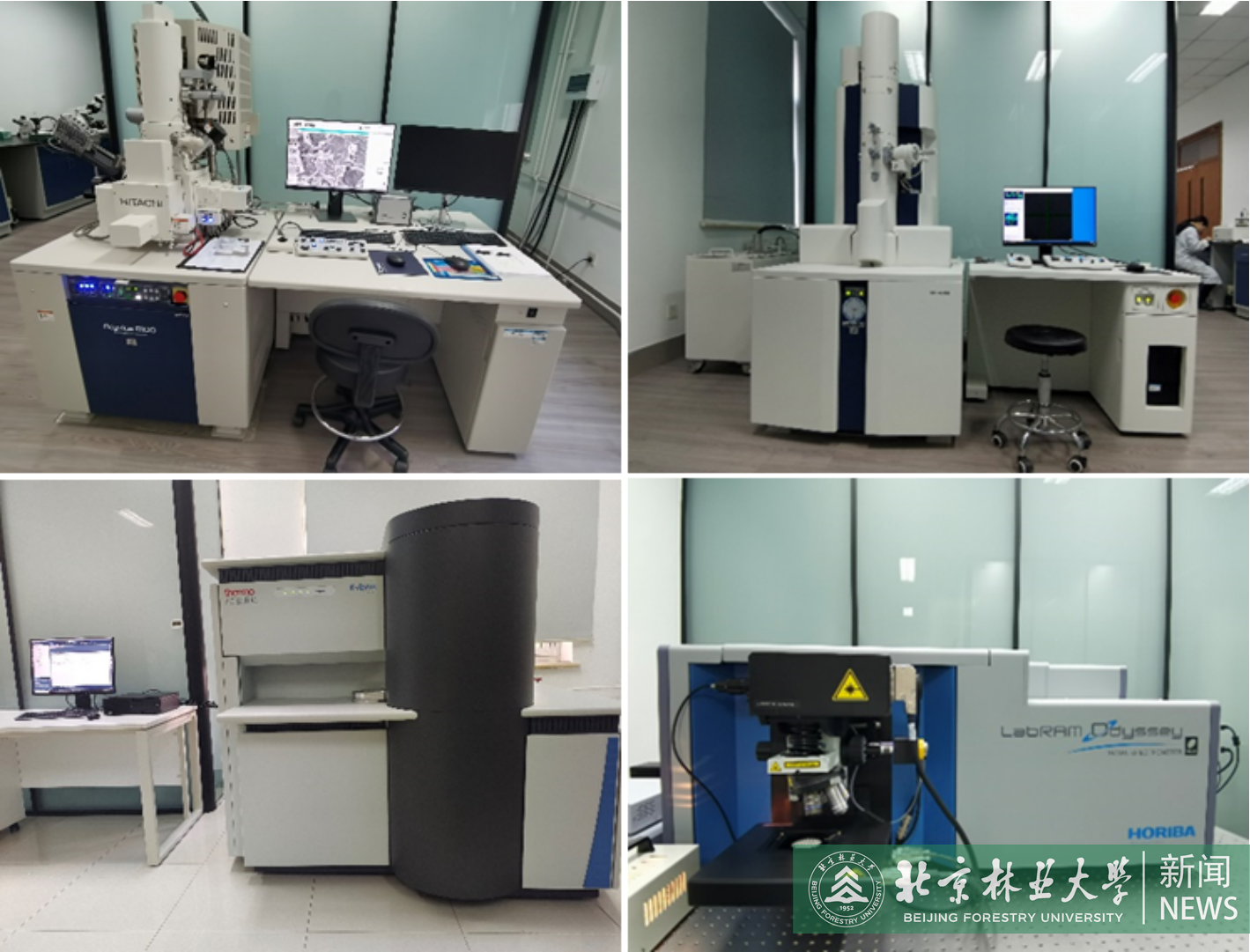 林木资源高值化利用创新平台开放运行2023.0301
林木资源高值化利用创新平台开放运行2023.0301 -
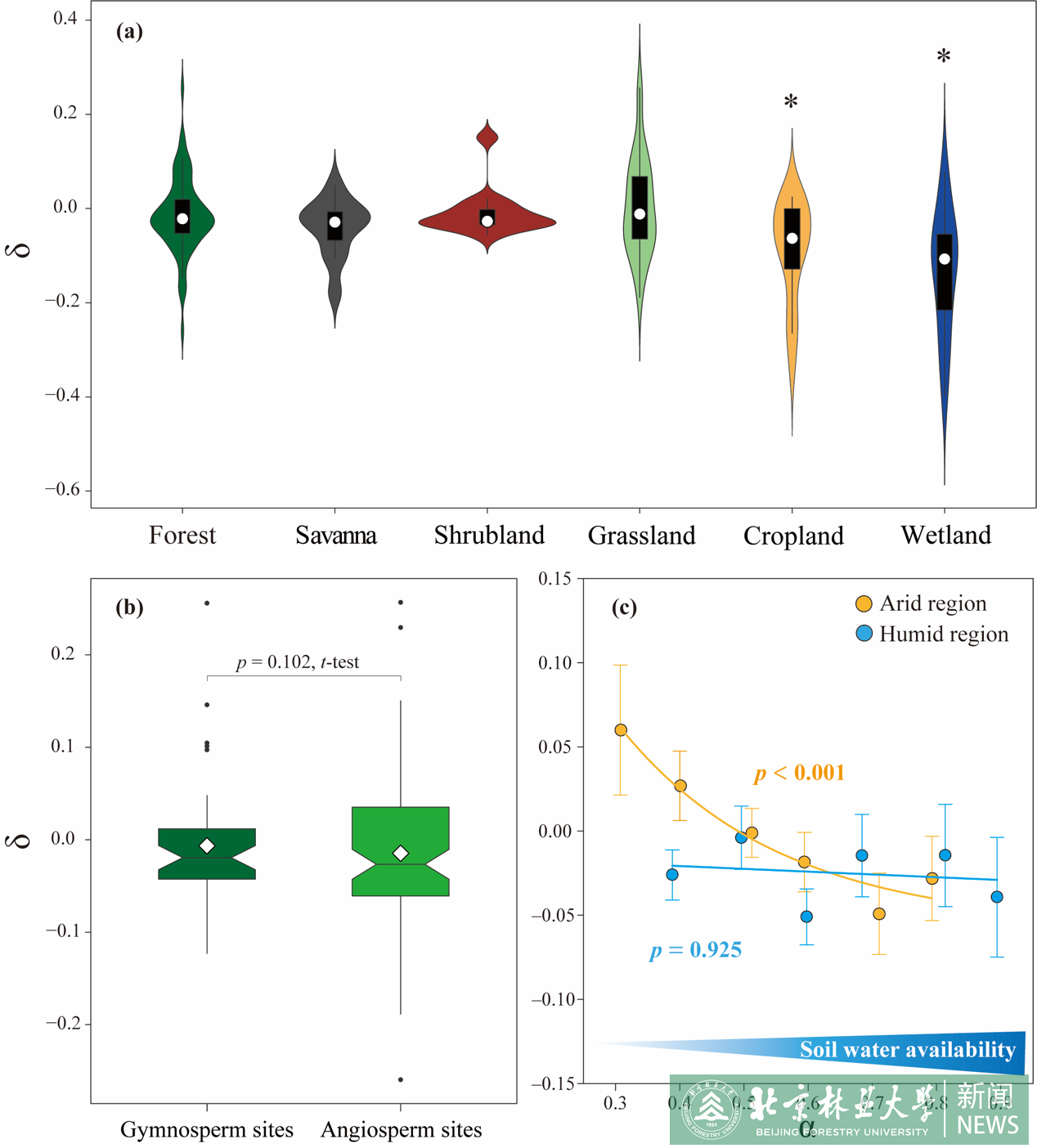 水保学院科研团队在气候变化下生态系统脆弱性领域取得进展2023.0228
水保学院科研团队在气候变化下生态系统脆弱性领域取得进展2023.0228 -
 我校加快教育数字化改革步伐2023.0223
我校加快教育数字化改革步伐2023.0223
更多
北林故事
更多
北林人物
-
 传承 奋进——我的育人故事讲述|翁强:我与学生共成长春风化雨,润物无声,三十多载世范人师,在新的历史时期,我要努力做塑造学生品格、品行、品味的“大先生”;做“为党育人、为国育才”的“四有”好老师!
传承 奋进——我的育人故事讲述|翁强:我与学生共成长春风化雨,润物无声,三十多载世范人师,在新的历史时期,我要努力做塑造学生品格、品行、品味的“大先生”;做“为党育人、为国育才”的“四有”好老师! -
更多北林故事
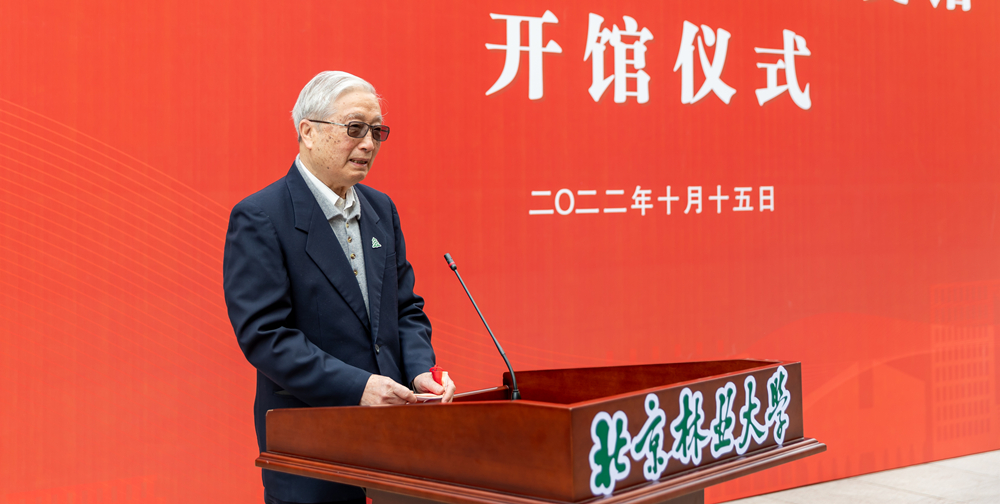 首届北林榜样:沈国舫少年勤学毅然回国,胸怀壮志俯首躬行。高高西山、茫茫林海,只为装点锦绣河山;三尺讲台、一方案牍,滋滋培育林业英才。从满头青丝到两鬓如霜,不变的是他为党育人为国育才的初心,永恒的是他坚守生态文明事业的理想。他,就是中国工程院院士沈国舫。
首届北林榜样:沈国舫少年勤学毅然回国,胸怀壮志俯首躬行。高高西山、茫茫林海,只为装点锦绣河山;三尺讲台、一方案牍,滋滋培育林业英才。从满头青丝到两鬓如霜,不变的是他为党育人为国育才的初心,永恒的是他坚守生态文明事业的理想。他,就是中国工程院院士沈国舫。